news
Mr Ibu: What to know about Blood Clot, cause of Ibu’s death
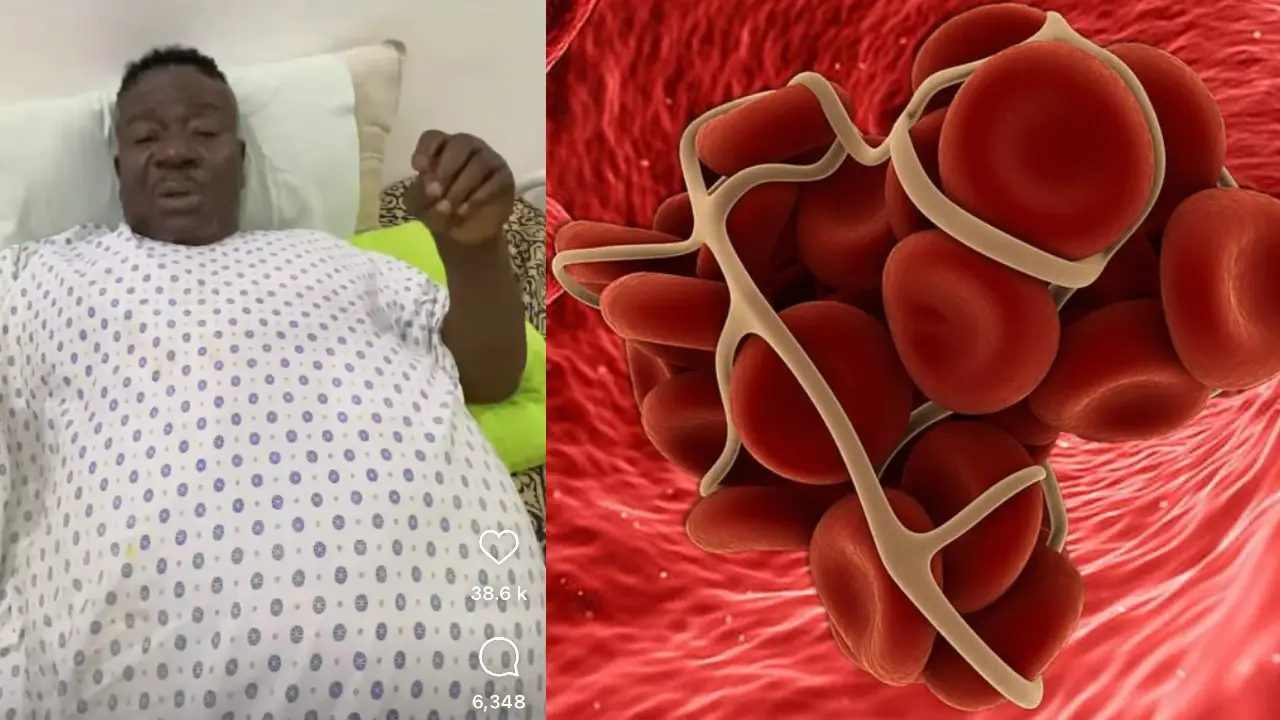
It is no news that popular Nollywood comic actor, John Okafor, also known as Mr Ibu lost battle to Blood clots disease last week.
These are what you need to know about the killer disease and how it ended Mr Ibu’s life.
See signs, symptoms and cure of Blood clots disease.
Understanding Blood Clots:
Blood clots, or thrombi, are clusters of blood that transform a liquid to a gel-like state. This coagulation process is a natural response to prevent blood vessels from leaking on the skin’s surface or within the body. Platelets and clotting factors, proteins in the blood, collaborate to form clots, halting bleeding.
Typically, blood clots dissolve when no longer needed. However, in some instances, clots may obstruct blood vessels or migrate to different body parts, called emboli. These situations can lead to various medical issues requiring immediate attention:
- Arterial embolism: A clot travels through an artery, disrupting blood supply to an organ or body part.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): A clot forms in veins, usually in the legs or arms.
- Heart attack: A clot develops to repair a damaged vessel near the heart, blocking blood supply.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE): A clot travels from a vein into the heart, potentially blocking blood supply to the lungs.
- Stroke: A blood clot moves into an artery supplying the brain, halting blood flow.
- Thrombophlebitis: Swelling occurs from a clot obstructing a vein.
Several factors, including medical conditions, medications, and habits, can heighten the risk of these complications. Conditions such as atrial fibrillation, cancer, diabetes, and lifestyle factors like inactivity or smoking contribute to the potential development of blood clots.
Causes of Blood Clots:
Blood clots naturally form as part of the body’s healing response to injuries, surgeries, or other medical procedures. They can also result from damage to arteries known as atherosclerosis. Some individuals may experience abnormal clotting due to age, genetics, or specific medical conditions.
Risk factors for blood clots include age (especially over 60), blood clotting disorders, certain medical conditions, hormonal influences like estrogen, inactivity, pregnancy, and smoking.
Symptoms of Blood Clots:
Symptoms of blood clots vary based on their location. Common signs include pain or tenderness, swelling, warmth, trouble speaking, vision changes, sudden headaches, chest pain, breathing difficulties, and coughing up blood.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots:
Doctors employ various methods to diagnose suspected blood clots, including physical exams, discussions about medical history and risk factors, blood tests to evaluate clotting factors, and imaging techniques like ultrasound and computed tomography (CT).
Blood Clot Treatment:
Treatment depends on the clot’s location, severity, and urgency. Urgent cases may involve thrombolytic drugs or medical procedures for clot removal. Less urgent situations may be addressed with blood thinners (anticoagulants or antiplatelets), and additional measures to mitigate future risks may be discussed.
A multidisciplinary team, including cardiologists, hematologists, interventional pulmonologists, interventional radiologists, neurologists, or vascular surgeons, may collaborate to provide comprehensive care. Specific blood clot treatments can be explored further through consultation with medical professionals.


















